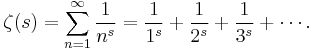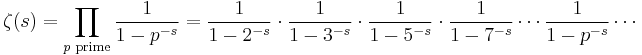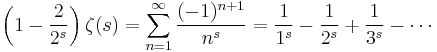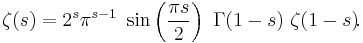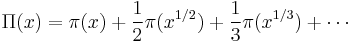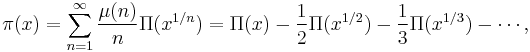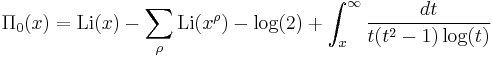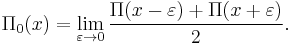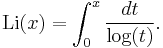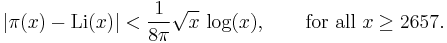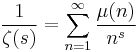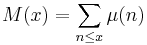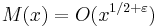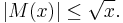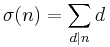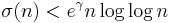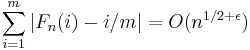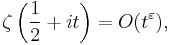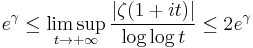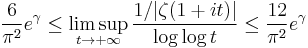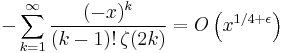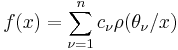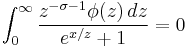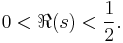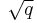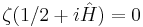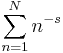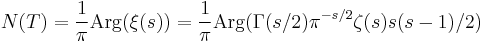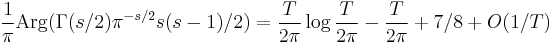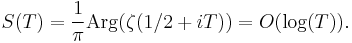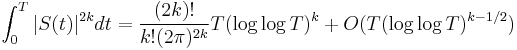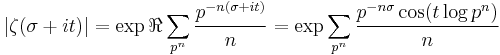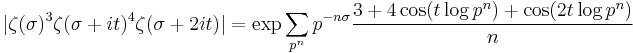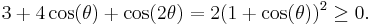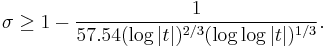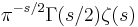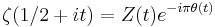Riemann hypothesis
| Millennium Prize Problems |
|---|
| P versus NP problem |
| Hodge conjecture |
| Poincaré conjecture (solution) |
| Riemann hypothesis |
| Yang–Mills existence and mass gap |
| Navier–Stokes existence and smoothness |
| Birch and Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture |
|
|
In mathematics, the Riemann hypothesis, proposed by Bernhard Riemann (1859), is a conjecture about the distribution of the zeros of the Riemann zeta-function which states that all non-trivial zeros of the Riemann zeta function have real part 1/2. The name is also used for some closely related analogues, such as the Riemann hypothesis for curves over finite fields.
The Riemann hypothesis implies results about the distribution of prime numbers that are in some ways as good as possible. Along with suitable generalizations, it is considered by some mathematicians to be the most important unresolved problem in pure mathematics (Bombieri 2000).
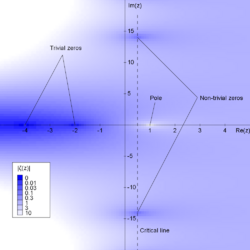
The Riemann zeta-function ζ(s) is defined for all complex numbers s ≠ 1. It has zeros at the negative even integers (i.e. at s = −2, −4, −6, ...). These are called the trivial zeros. The Riemann hypothesis is concerned with the non-trivial zeros, and states that:
- The real part of any non-trivial zero of the Riemann zeta function is 1/2.
Thus the non-trivial zeros should lie on the critical line, 1/2 + it, where t is a real number and i is the imaginary unit.
The Riemann hypothesis is part of Problem 8, along with the Goldbach conjecture, in Hilbert's list of 23 unsolved problems, and is also one of the Clay Mathematics Institute Millennium Prize Problems. Since it was formulated, it has withstood concentrated efforts from many outstanding mathematicians. In 1973, Pierre Deligne proved that the Riemann hypothesis held true over finite fields. The full version of the hypothesis remains unsolved, although modern computer calculations have shown that the first 10 trillion zeros lie on the critical line.
There are several popular books on the Riemann hypothesis, such as Derbyshire (2003), Rockmore (2005), Sabbagh (2003), du Sautoy (2003). The books Edwards (1974), Patterson (1988) and Borwein et al. (2008) give mathematical introductions, while Titchmarsh (1986), Ivić (1985) and Karatsuba & Voronin (1992) are advanced monographs.
Contents |
The Riemann zeta function
The Riemann zeta function is given for complex s with real part greater than 1 by
Leonhard Euler showed that it is given by the Euler product
where the infinite product extends over all prime numbers p, and again converges for complex s with real part greater than 1. The convergence of the Euler product shows that ζ(s) has no zeros in this region, as none of the factors have zeros.
The Riemann hypothesis discusses zeros outside the region of convergence of this series, so it needs to be analytically continued to all complex s. This can be done by expressing it in terms of the Dirichlet eta function as follows. If s has positive real part, then the zeta function satisfies
where the series on the right converges whenever s has positive real part. Thus, this alternative series extends the zeta function from Re(s) > 1 to the larger domain Re(s) > 0.
In the strip 0 < Re(s) < 1 the zeta function satisfies the functional equation
One may then define ζ(s) for all remaining nonzero complex numbers s by assuming that this equation holds outside the strip as well, and letting ζ(s) equal the right-hand side of the equation whenever s has non-positive real part. If s is a negative even integer then ζ(s) = 0 because the factor sin(πs/2) vanishes; these are the trivial zeros of the zeta function. (If s is a positive even integer this argument does not apply because the zeros of sin are cancelled by the poles of the gamma function.) The value ζ(0) = −1/2 is not determined by the functional equation, but is the limiting value of ζ(s) as s approaches zero. The functional equation also implies that the zeta function has no zeros with negative real part other than the trivial zeros, so all non-trivial zeros lie in the critical strip where s has real part between 0 and 1.
History
"…es ist sehr wahrscheinlich, dass alle Wurzeln reell sind. Hiervon wäre allerdings ein strenger Beweis zu wünschen; ich habe indess die Aufsuchung desselben nach einigen flüchtigen vergeblichen Versuchen vorläufig bei Seite gelassen, da er für den nächsten Zweck meiner Untersuchung entbehrlich schien."
"…it is very probable that all roots are real. Of course one would wish for a rigorous proof here; I have for the time being, after some fleeting vain attempts, provisionally put aside the search for this, as it appears dispensable for the next objective of my investigation."
In his 1859 paper On the Number of Primes Less Than a Given Magnitude Riemann found an explicit formula for the number of primes π(x) less than a given number x. His formula was given in terms of the related function
which counts primes where a prime power pn counts as 1/n of a prime. The number of primes can be recovered from this function by
where μ is the Möbius function. Riemann's formula is then
where the sum is over the nontrivial zeros of the zeta function and where Π0 is a slightly modified version of Π that replaces its value at its points of discontinuity by the average of its upper and lower limits:
The summation in Riemann's formula is not absolutely convergent, but may be evaluated by taking the zeros ρ in order of the absolute value of their imaginary part. The function Li occurring in the first term is the (unoffset) logarithmic integral function given by the Cauchy principal value of the divergent integral
The terms Li(xρ) involving the zeros of the zeta function need some care in their definition as Li has branch points at 0 and 1, and are defined (for x > 1) by analytic continuation in the complex variable ρ in the region Re(ρ) > 0, i.e. they should be considered as Ei(ρ ln x). The other terms also correspond to zeros: the dominant term Li(x) comes from the pole at s = 1, considered as a zero of multiplicity −1, and the remaining small terms come from the trivial zeros. For some graphs of the sums of the first few terms of this series see Riesel & Göhl (1970) or Zagier (1977).
This formula says that the zeros of the Riemann zeta function control the oscillations of primes around their "expected" positions. Riemann knew that the non-trivial zeros of the zeta-function were symmetrically distributed about the line s = 1/2 + it, and he knew that all of its non-trivial zeros must lie in the range 0 ≤ Re(s) ≤ 1. He checked that a few of the zeros lay on the critical line with real part 1/2 and suggested that they all do; this is the Riemann hypothesis.
Consequences of the Riemann hypothesis
The practical uses of the Riemann hypothesis include many propositions which are known to be true under the Riemann hypothesis, and some which can be shown to be equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis.
Distribution of prime numbers
Riemann's explicit formula for the number of primes less than a given number in terms of a sum over the zeros of the Riemann zeta function says that the magnitude of the oscillations of primes around their expected position is controlled by the real parts of the zeros of the zeta function. In particular the error term in the prime number theorem is closely related to the position of the zeros: for example, the supremum of real parts of the zeros is the infimum of numbers β such that the error is O(xβ) (Ingham 1932).
Von Koch (1901) proved that the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to the "best possible" bound for the error of the prime number theorem.
A precise version of Koch's result, due to Schoenfeld (1976), says that the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to
Growth of arithmetic functions
The Riemann hypothesis implies strong bounds on the growth of many other arithmetic functions, in addition to the primes counting function above.
One example involves the Möbius function μ. The statement that the equation
is valid for every s with real part greater than ½, with the sum on the right hand side converging, is equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis. From this we can also conclude that if the Mertens function is defined by
then the claim that
for every positive ε is equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis (Titchmarsh 1986). (For the meaning of these symbols, see Big O notation.) The determinant of the order n Redheffer matrix is equal to M(n), so the Riemann hypothesis can also be stated as a condition on the growth of these determinants. The Riemann hypothesis puts a rather tight bound on the growth of M, since Odlyzko & te Riele (1985) disproved the slightly stronger Mertens conjecture
The Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to many other conjectures about the rate of growth of other arithmetic functions aside from μ(n). A typical example is Robin's theorem (Robin 1984), which states that if σ(n) is the divisor function, given by
then
for all n > 5040 if and only if the Riemann hypothesis is true.
Another example was found by Franel & Landau (1924) showing that the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to a statement that the terms of the Farey sequence are fairly regular. More precisely, if Fn is the Farey sequence of order n, beginning with 1/n and up to 1/1, then the claim that for all ε > 0
is equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis. Here 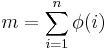 is the number of terms in the Farey sequence of order n.
is the number of terms in the Farey sequence of order n.
For an example from group theory, if g(n) is Landau's function given by the maximal order of elements of the symmetric group Sn of degree n, then Massias, Nicolas & Robin (1988) showed that the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to the bound
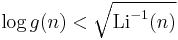 for all sufficiently large n.
for all sufficiently large n.
Lindelöf hypothesis and growth of the zeta function
The Riemann hypothesis has various weaker consequences as well; one is the Lindelöf hypothesis on the rate of growth of the zeta function on the critical line, which says that, for any ε > 0,
as t tends to infinity.
The Riemann hypothesis also implies quite sharp bounds for the growth rate of the zeta function in other regions of the critical strip. For example, it implies that
so the growth rate of ζ(1+it) and its inverse would be known up to a factor of 2 (Titchmarsh 1986).
Large prime gap conjecture
The prime number theorem implies that on average, the gap between the prime p and its successor is log p. However, some gaps between primes may be much larger than the average. Cramér proved that, assuming the Riemann hypothesis, every gap is O(√p log p). This is a case when even the best bound that can currently be proved using the Riemann hypothesis is far weaker than what seems to be true: Cramér's conjecture implies that every gap is O(log(p)2) which, while larger than the average gap, is far smaller than the bound implied by the Riemann hypothesis. Numerical evidence supports Cramér's conjecture (Nicely 1999).
Criteria equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis
Many statements equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis have been found, though so far none of them have led to much progress in solving it. Some typical examples are as follows.
The Riesz criterion was given by Riesz (1916), to the effect that the bound
holds for all 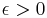 if and only if the Riemann hypothesis holds.
if and only if the Riemann hypothesis holds.
Nyman (1950) proved that the Riemann Hypothesis is true if and only if the space of functions of the form
where ρ(z) is the fractional part of z, 0 ≤ θν ≤ 1, and
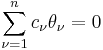 ,
,
is dense in the Hilbert space L2(0,1) of square-integrable functions on the unit interval. Beurling (1955) extended this by showing that the zeta function has no zeros with real part greater than 1/p if and only if this function space is dense in Lp(0,1)
Salem (1953) showed that the Riemann hypothesis is true if and only if the integral equation
has no non-trivial bounded solutions φ for 1/2<σ<1.
Weil's criterion is the statement that the positivity of a certain function is equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis. Related is Li's criterion, a statement that the positivity of a certain sequence of numbers is equivalent to the Riemann hypothesis.
Speiser (1934) proved that the Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to the statement that 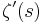 , the derivative of
, the derivative of 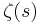 , has no zeros in the strip
, has no zeros in the strip
That ζ has only simple zeros on the critical line is equivalent to its derivative having no zeros on the critical line.
Consequences of the generalized Riemann hypothesis
Several applications use the generalized Riemann hypothesis for Dirichlet L-series rather than just the Riemann hypothesis. Many properties of the Riemann zeta function can easily be generalized to all Dirichlet L-series, so it is plausible that a method that proves the Riemann hypothesis for the Riemann zeta function would also work for the generalized Riemann hypothesis. Several results first proved using the generalized Riemann hypothesis were later given unconditional proofs without using it, though these were usually much harder. Many of the consequences on the following list are taken from Conrad (2010).
- In 1913, Gronwall showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that Gauss's list of imaginary quadratic fields with class number 1 is complete, though Baker, Stark and Heegner later gave unconditional proofs of this without using the generalized Riemann hypothesis.
- In 1917, Hardy and Littlewood showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies a conjecture of Chebyshev that
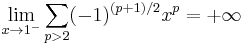
- which says that in some sense primes 3 mod 4 are more common than primes 1 mod 4.
- In 1923 Hardy and Littlewood showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies a weak form of the Goldbach conjecture for odd numbers: that every sufficiently large odd number at is the sum of 3 primes, though in 1937 Vinogradov gave an unconditional proof. In 1997 Deshouillers, Effinger, te Riele, and Zinoviev showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that every odd number greater than 5 at is the sum of 3 primes.
- In 1934, Chowla showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that the first prime in the arithmetic progression a mod m is at most Km2log(m)2 for some fixed constant K.
- In 1967, Hooley showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies Artin's conjecture on primitive roots.
- In 1973, Weinberger showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that Euler's list of idoneal numbers is complete.
- Weinberger (1973) showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis for the zeta-functions of all algebraic number fields implies that any number field with class number 1 is either Euclidean or an imaginary quadratic number field of discriminant −19, −43, −67, or −163.
- In 1976, Miller showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that one can test if a number is prime in polynomial times. In 2002, Manindra Agrawal, Neeraj Kayal and Nitin Saxena proved this result unconditionally using the AKS primality test.
- In 1997 Ono and Soundararajan showed that the generalized Riemann hypothesis implies that Ramanujan's integral quadratic form x2 +y2 + 10z2 represents all integers that it represents locally, with exactly 18 exceptions.
Generalizations and analogues of the Riemann hypothesis
Dirichlet L-series and other number fields
The Riemann hypothesis can be generalized by replacing the Riemann zeta-function by the formally similar, but much more general, global L-functions. In this broader setting, one expects the non-trivial zeros of the global L-functions to have real part 1/2. It is these conjectures, rather than the classical Riemann hypothesis only for the single Riemann zeta-function, which accounts for the true importance of the Riemann hypothesis in mathematics.
The generalized Riemann hypothesis extends the Riemann hypothesis to all Dirichlet L-functions. In particular it implies the conjecture that Siegel zeros (zeros of L functions between 1/2 and 1) do not exist.
The extended Riemann hypothesis extends the Riemann hypothesis to all Dedekind zeta-functions of algebraic number fields. The extended Riemann hypothesis for abelian extension of the rationals is equivalent to the generalized Riemann hypothesis. The Riemann hypothesis can also be extended to the L-functions of Hecke characters of number fields.
The grand Riemann hypothesis extends it to all automorphic zeta functions, such as Mellin transforms of Hecke eigenforms.
Function fields and zeta functions of varieties over finite fields
Artin (1924) introduced global zeta-functions of (quadratic) function fields and conjectured an analogue of the Riemann hypothesis for them, which has been proven by Hasse in the genus 1 case and by Weil (1948) in general. For instance, the fact that the Gauss sum, of the quadratic character of a finite field of size q (with q odd), has absolute value
is actually an instance of the Riemann hypothesis in the function field setting. This led Weil (1949) to conjecture a similar statement for all algebraic varieties; the resulting Weil conjectures were proven by Pierre Deligne (1974, 1980).
Selberg zeta functions
Selberg (1956) introduced the Selberg zeta function of a Riemann surface. These are similar to the Riemann zeta function: they have a functional equation, and an infinite product similar to the Euler product but taken over closed geodesics rather than primes. The Selberg trace formula is the analogue for these functions of the explicit formulas in prime number theory. Selberg proved that the Selberg zeta functions satisfy the analogue of the Riemann hypothesis, with the imaginary parts of their zeros related to the eigenvalues of the Laplacian operator of the Riemann surface.
Ihara zeta functions
The Ihara zeta function of a finite graph is an analogue of the Selberg zeta function introduced by Yasutaka Ihara. A regular finite graph is a Ramanujan graph, a mathematical model of efficient communication networks, if and only if its Ihara zeta function satisfies the analogue of the Riemann hypothesis as was pointed out by T. Sunada.
Montgomery's pair correlation conjecture
Montgomery (1973) suggested the pair correlation conjecture that the correlation functions of the (suitably normalized) zeros of the zeta function should be the same as those of the eigenvalues of a random hermitian matrix. Odlyzko (1987) showed that this is supported by large scale numerical calculations of these correlation functions.
Montgomery showed that (assuming the Riemann hypothesis) at least 2/3 of all zeros are simple, and a related conjecture is that all zeros of the zeta function are simple (or more generally have no non-trivial integer linear relations between their imaginary parts). Dedekind zeta functions of algebraic number fields, which generalize the Riemann zeta function, often do have multiple complex zeros. This is because the Dedekind zeta functions factorize as a product of powers of Artin L-functions, so zeros of Artin L-functions sometimes give rise to multiple zeros of Dedekind zeta functions. Other examples of zeta functions with multiple zeros are the L-functions of some elliptic curves: these can have multiple zeros at the real point of their critical line; the Birch-Swinnerton-Dyer conjecture predicts that the multiplicity of this zero is the rank of the elliptic curve.
Other zeta functions
There are many other examples of zeta functions with analogues of the Riemann hypothesis, some of which have been proved. Goss zeta functions of function fields have a Riemann hypothesis, proved by Sheats (1998). The main conjecture of Iwasawa theory, proved by Barry Mazur and Andrew Wiles for cyclotomic fields, and Wiles for totally real fields, identifies the zeros of a p-adic L-function with the eigenvalues of an operator, so can be thought of as an analogue of the Hilbert–Pólya conjecture for p-adic L-functions (Wiles 2000).
Attempts to prove the Riemann hypothesis
Several mathematicians have addressed the Riemann hypothesis, but none of their attempts have yet been accepted as correct solutions. Watkins (2007) lists some incorrect solutions, and more are frequently announced.
Operator theory
Hilbert and Polya suggested that one way to derive the Riemann hypothesis would be to find a self-adjoint operator, from the existence of which the statement on the real parts of the zeros of ζ(s) would follow when one applies the criterion on real eigenvalues. Some support for this idea comes from several analogues of the Riemann zeta functions whose zeros correspond to eigenvalues of some operator: the zeros of a zeta function of a variety over a finite field correspond to eigenvalues of a Frobenius element on an etale cohomology group, the zeros of a Selberg zeta function are eigenvalues of a Laplacian operator of a Riemann surface, and the zeros of a p-adic zeta function correspond to eigenvectors of a Galois action on ideal class groups.
Odlyzko (1987) showed that the distribution of the zeros of the Riemann zeta function shares some statistical properties with the eigenvalues of random matrices drawn from the Gaussian unitary ensemble. This gives some support to the Hilbert–Pólya conjecture.
In 1999, Michael Berry and Jon Keating conjectured that there is some unknown quantization 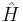 of the classical Hamiltonian
of the classical Hamiltonian 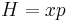 so that
so that
and even more strongly, that the Riemann zeros coincide with the spectrum of the operator 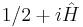 . This is to be contrasted to canonical quantization which leads to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle
. This is to be contrasted to canonical quantization which leads to the Heisenberg uncertainty principle ![[x,p]=1/2](/2010-wikipedia_en_wp1-0.8_orig_2010-12/I/b79a061362e71cdfe458a526cc1f61aa.png) and the natural numbers as spectrum of the quantum harmonic oscillator. The crucial point is that the Hamiltonian should be a self-adjoint operator so that the quantization would be a realization of the Hilbert–Pólya program. In a connection with this Quantum mechanical problem Berry and Connes had proposed that the inverse of the potential of the Hamiltonian is connected to the half-derivative of the function
and the natural numbers as spectrum of the quantum harmonic oscillator. The crucial point is that the Hamiltonian should be a self-adjoint operator so that the quantization would be a realization of the Hilbert–Pólya program. In a connection with this Quantum mechanical problem Berry and Connes had proposed that the inverse of the potential of the Hamiltonian is connected to the half-derivative of the function 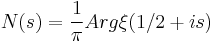 then, in Berry-Connes approach
then, in Berry-Connes approach 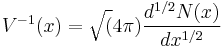 (Connes 1999).
(Connes 1999).
The analogy with the Riemann hypothesis over finite fields suggests that the Hilbert space containing eigenvectors corresponding to the zeros might be some sort of first cohomology group of the spectrum Spec(Z) of the integers. Deninger (1998) described some of the attempts to find such a cohomology theory.
Zagier (1983) constructed a natural space of invariant functions on the upper half plane which has eigenvalues under the Laplacian operator corresponding to zeros of the Riemann zeta function, and remarked that in the unlikely event that one could show the existence of a suitable positive definite inner product on this space the Riemann hypothesis would follow. Cartier (1982) discussed a related example, where due to a bizarre bug a computer program listed zeros of the Riemann zeta function as eigenvalues of the same Laplacian operator.
Lee-Yang theorem
The Lee-Yang theorem states that the zeros of certain partition functions in statistical mechanics all lie on a "critical line" with real part 0, and this has led to some speculation about a relationship with the Riemann hypothesis (Knauf 1999).
Turán's result
Pál Turán (1948) showed that if the functions
have no zeros when the real part of s is greater than one then
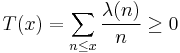 for all x > 0,
for all x > 0,
where λ(n) is the Liouville function given by (−1)r if n has r prime factors. He showed that this in turn would imply that the Riemann hypothesis is true. However Haselgrove (1958) proved that T(x) is negative for infinitely many x (and also disproved the closely related Polya conjecture), and Borwein, Ferguson & Mossinghoff (2008) showed that the smallest such x is 72185376951205. Spira (1968) showed by numerical calculation that the finite Dirichlet series above for N=19 has a zero with real part greater than 1. Turán also showed that a somewhat weaker assumption, the nonexistence of zeros with real part greater than 1+N−1/2+ε for large N in the finite Dirichlet series above, would also imply the Riemann hypothesis, but Montgomery (1983) showed that for all sufficiently large N these series have zeros with real part greater than 1 + (log log N)/(4 log N). Therefore, Turán's result is vacuously true and cannot be used to help prove the Riemann hypothesis.
Noncommutative geometry
Connes (1999, 2000) has described a relationship between the Riemann hypothesis and noncommutative geometry, and shows that a suitable analogue of the Selberg trace formula for the action of the idèle class group on the adèle class space would imply the Riemann hypothesis. Some of these ideas are elaborated in Lapidus (2008).
Hilbert spaces of entire functions
Louis de Branges (1992) showed that the Riemann hypothesis would follow from a positivity condition on a certain Hilbert space of entire functions. However Conrey & Li (2000) showed that the necessary positivity conditions are not satisfied.
Quasicrystals
The Riemann hypothesis implies that the zeros of the zeta function form a quasicrystal, meaning a distribution with discrete support whose Fourier transform also has discrete support. Dyson (2009) suggested trying to prove the Riemann hypothesis by classifying, or at least studying, 1-dimensional quasicrystals.
Multiple zeta functions
Deligne's proof of the Riemann hypothesis over finite fields used the zeta functions of product varieties, whose zeros and poles correspond to sums of zeros and poles of the original zeta function, in order to bound the real parts of the zeros of the original zeta function. By analogy, Kurokawa (1992) introduced multiple zeta functions whose zeros and poles correspond to sums of zeros and poles of the Riemann zeta function. To make the series converge he restricted to sums of zeros or poles all with non-negative imagianry part. So far, the known bounds on the zeros and poles of the multiple zeta functions are not strong enough to give useful estimates for the zeros of the Riemann zeta function.
Location of the zeros
Number of zeros
The functional equation combined with the argument principle implies that the number of zeros of the zeta function with imaginary part between 0 and T is given by
for s=1/2+iT, where the argument is defined by varying it continuously along the line with Im(s)=T, starting with argument 0 at ∞+iT. This is the sum of a large but well understood term
and a small but rather mysterious term
So the density of zeros with imaginary part near T is about log(T)/2π, and the function S describes the small deviations from this. The function S(t) jumps by 1 at each zero of the zeta function, and for t ≥ 8 it decreases monotonically between zeros with derivative close to −log t.
Selberg (1946) showed that the average moments of even powers of S are given by
and Odlyzko (1992, 2.5) pointed out that this implies that S(T)/(log log T)1/2 resembles a Gaussian random variable with mean 0 and variance 2π2. In particular |S(T)| is usually somewhere around (log log T)1/2, but occasionally much larger. The exact order of growth of S(T) is not known. There has been no unconditional improvement to Riemann's original bound S(T)=O(log T), though the Riemann hypothesis implies the slightly smaller bound S(T)=O(log T/log log T) (Titchmarsh 1985). The true order of magnitude may be somewhat less than this, as random functions with the same distribution as S(T) tend to have growth of order about log(T)1/2. In the other direction it cannot be too small: Selberg (1946) showed that S(T) ≠ o((log T)1/3/(log log T)7/3), and assuming the Riemann hypothesis Montgomery showed that S(T) ≠ o((log T)1/2/(log log T)1/2).
Numerical calculations confirm that S grows very slowly: |S(T)| < 1 for T < 280, |S(T)| < 2 for T < 6800000, and the largest value of |S(T)| found so far is not much larger than 3 (Odlyzko 2002).
Riemann's estimate S(T) = O(log T) implies that the gaps between zeros are bounded, and Littlewood improved this slightly, showing that the gaps between their imaginary parts tends to 0.
The theorem of Hadamard and de la Vallée-Poussin
Hadamard (1896) and de la Vallée-Poussin (1896) independently proved that no zeros could lie on the line Re(s) = 1. Together with the functional equation and the fact that there are no zeros with real part greater than 1, this showed that all non-trivial zeros must lie in the interior of the critical strip 0 < Re(s) < 1. This was a key step in their first proofs of the prime number theorem.
Both the original proofs that the zeta function has no zeros with real part 1 are similar, and depend on showing that if ζ(1+it) vanishes, then ζ(1+2it) is singular, which is not possible. One way of doing this is by using the inequality
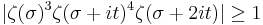 for σ>1, t real,
for σ>1, t real,
and looking at the limit as σ tends to 1. This inequality follows by taking the real part of the log of the Euler product to see that
(where the sum is over all prime powers pn) so that
which is at least 1 because all the terms in the sum are positive, due to the inequality
Zero-free regions
De la Vallée-Poussin (1899-1900) proved that if σ+it is a zero of the Riemann zeta function, then 1-σ ≥ C/log(t) for some positive constant C. In other words zeros cannot be too close to the line σ=1: there is a zero-free region close to this line. This zero-free region has been enlarged by several authors. Ford (2002) gave a version with explicit numerical constants: ζ(σ + it) ≠ 0 whenever |t| ≥ 3 and
Zeros on the critical line
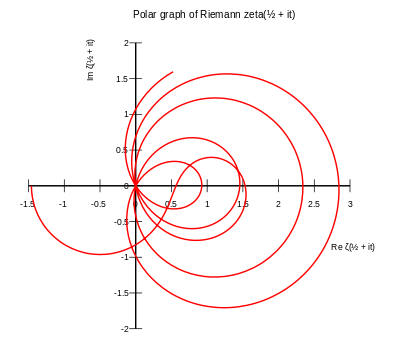
Hardy (1914) and Hardy & Littlewood (1921) showed there are infinitely many zeros on the critical line, by considering moments of certain functions related to the zeta function. Selberg (1942) proved that at least a (small) positive proportion of zeros lie on the line. Levinson (1974) improved this to one-third of the zeros by relating the zeros of the zeta function to those of its derivative, and Conrey (1989) improved this further to two-fifths.
Most zeros lie close to the critical line. More precisely, Bohr & Landau (1914) showed that for any positive ε, all but an infinitely small proportion of zeros lie within a distance ε of the critical line. Ivić (1985) gives several more precise versions of this result, called zero density estimates, which bound the number of zeros in regions with imaginary part at most T and real part at least 1/2+ε.
Numerical calculations
The function
has the same zeros as the zeta function in the critical strip, and is real on the critical line because of the functional equation, so one can prove the existence of zeros exactly on the real line between two points by checking numerically that the function has opposite signs at these points. Usually one writes
where Hardy's function Z and the Riemann-Siegel theta function θ are uniquely defined by this and the condition that they are smooth real functions with θ(0)=0. By finding many intervals where the function Z changes sign one can show that there are many zeros on the critical line. To verify the Riemann hypothesis up to a given imaginary part T of the zeros, one also has to check that there are no further zeros off the line in this region. This can be done by calculating the total number of zeros in the region and checking that it is the same as the number of zeros found on the line. This allows one to verify the Riemann hypothesis computationally up to any desired value of T (provided all the zeros of the zeta function in this region are simple and on the critical line).
Some calculations of zeros of the zeta function are listed below. So far all zeros that have been checked are on the critical line and are simple. (A multiple zero would cause problems for the zero finding algorithms, which depend on finding sign changes between zeros.) For tables of the zeros, see Haselgrove & Miller (1960) or Odlyzko.
| Year | Number of zeros | Author |
|---|---|---|
| 1859? | 3 | B. Riemann used the Riemann-Siegel formula (unpublished, but reported in Siegel 1932). |
| 1903 | 15 | J. P. Gram (1903) used Euler-Maclaurin summation and discovered Gram's law. He showed that all 10 zeros with imaginary part at most 50 range lie on the critical line with real part 1/2 by computing the sum of the inverse 10th powers of the roots he found. |
| 1914 | 79 (γn ≤ 200) | R. J. Backlund (1914) introduced a better method of checking all the zeros up to that point are on the line, by studying the argument S(T) of the zeta function. |
| 1925 | 138 (γn ≤ 300) | J. I. Hutchinson (1925) found the first failure of Gram's law, at the Gram point g126. |
| 1935 | 195 | E. C. Titchmarsh (1935) used the recently rediscovered Riemann-Siegel formula, which is much faster than Euler-Maclaurin summation.It takes about O(T3/2+ε) steps to check zeros with imaginary part less than T, while the Euler-Maclaurin method takes about O(T2+ε) steps. |
| 1936 | 1041 | E. C. Titchmarsh (1936) and L. J. Comrie were the last to find zeros by hand. |
| 1953 | 1104 | A. M. Turing (1953) found a more efficient way to check that all zeros up to some point are accounted for by the zeros on the line, by checking that Z has the correct sign at several consecutive Gram points and using the fact that S(T) has average value 0. This requires almost no extra work because the sign of Z at Gram points is already known from finding the zeros, and is still the usual method used. This was the first use of a digital computer to calculate the zeros. |
| 1956 | 15000 | D. H. Lehmer (1956) discovered a few cases where the zeta function has zeros that are "only just" on the line: two zeros of the zeta function are so close together that it is unusually difficult to find a sign change between them. This is called "Lehmer's phenomenon", and first occurs at the zeros with imaginary parts 7005.063 and 7005.101, which differ by only .04 while the average gap between other zeros near this point is about 1. |
| 1956 | 25000 | D. H. Lehmer |
| 1958 | 35337 | N. A. Meller |
| 1966 | 250000 | R. S. Lehman |
| 1968 | 3500000 | Rosser, Yohe & Schoenfeld (1969) stated Rosser's rule (described below). |
| 1977 | 40000000 | R. P. Brent |
| 1979 | 81000001 | R. P. Brent |
| 1982 | 200000001 | R. P. Brent, J. van de Lune, H. J. J. te Riele, D. T. Winter |
| 1983 | 300000001 | J. van de Lune, H. J. J. te Riele |
| 1986 | 1500000001 | van de Lune, te Riele & Winter (1986) gave some statistical data about the zeros and give several graphs of Z at places where it has unusual behavior. |
| 1987 | A few of large height | A. M. Odlyzko (1987) computed smaller numbers of zeros of much larger height, around 1012, to high precision to check Montgomery's pair correlation conjecture. |
| 1992 | A few of large height | A. M. Odlyzko (1992) computed a few zeros of heights up to 1020, and gave an extensive discussion of the results. |
| 2001 | 10000000000 | J. van de Lune (unpublished) |
| 2004 | 900000000000 | S. Wedeniwski (ZetaGrid distributed computing) |
| 2004 | 10000000000000 | X. Gourdon (2004) and Patrick Demichel used the Odlyzko–Schönhage algorithm. They also checked a few zeros of much larger height. |
Gram points
A Gram point is a value of t such that ζ(1/2 + it) = Z(t)e − iθ(t) is a non-zero real; these are easy to find because they are the points where the Euler factor at infinity π−s/2Γ(s/2) is real at s = 1/2 + it, or equivalently θ(t) is a multiple nπ of π. They are usually numbered as gn for n = −1, 0, 1, ..., where gn is the unique solution of θ(t) = nπ with t ≥ 8 (θ is increasing beyond this point; there is a second point with θ(t) = −π near 3.4, and θ(0) = 0). Gram observed that there was often exactly one zero of the zeta function between any two Gram points; Hutchinson called this observation Gram's law. There are several other closely related statements that are also sometimes called Gram's law: for example, (−1)nZ(gn) is usually positive, or Z(t) usually has opposite sign at consecutive Gram points. The imaginary parts γn of the first few zeros (in blue) and the first few Gram points gn are given in the following table
| g−1 | γ1 | g0 | γ2 | g1 | γ3 | g2 | γ4 | g3 | γ5 | g4 | γ6 | g5 | ||
| 0 | 3.4 | 9.667 | 14.135 | 17.846 | 21.022 | 23.170 | 25.011 | 27.670 | 30.425 | 31.718 | 32.935 | 35.467 | 37.586 | 38.999 |
The first failure of Gram's law occurs at the 127'th zero and the Gram point g126, which are in the "wrong" order.
| g124 | γ126 | g125 | g126 | γ127 | γ128 | g127 | γ129 | g128 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 279.148 | 279.229 | 280.802 | 282.455 | 282.465 | 283.211 | 284.104 | 284.836 | 285.752 |
A Gram point t is called good if the zeta function is positive at 1/2 + it. The indices of the "bad" Gram points where Z has the "wrong" sign are 126, 134, 195, 211,... (sequence A114856 in OEIS). A Gram block is an interval bounded by two good Gram points such that all the Gram points between them are bad. A refinement of Gram's law called Rosser's rule due to Rosser, Yohe & Schoenfeld (1969) says that Gram blocks often have the expected number of zeros in them (the same as the number of Gram intervals), even though some of the individual Gram intervals in the block may not have exactly one zero in them. For example, the interval bounded by g125 and g127 is a Gram block containing a unique bad Gram point g126, and contains the expected number 2 of zeros although neither of its two Gram intervals contains a unique zero. Rosser et al. checked that there were no exceptions to Rosser's rule in the first 3 million zeros, though there are infinitely many exceptions for larger imaginary part.
Gram's rule and Rosser's rule both say that in some sense zeros do not stray too far from their expected positions. The distance of a zero from its expected position is controlled by the function S defined above, which grows extremely slowly: its average value is of the order of (log log T)1/2, which only reaches 2 for T around 1024. This means that both rules hold most of the time for small T but eventually break down often.
Arguments for and against the Riemann hypothesis
Mathematical papers about the Riemann hypothesis tend to be cautiously noncommittal about its truth. Of authors who express an opinion, most of them, such as Riemann (1859) or Bombieri (2000), imply that they expect (or at least hope) that it is true. The few authors who express serious doubt about it include Ivić (2008) who lists some reasons for being skeptical, and Littlewood (1962) who flatly states that he believes it to be false, and that there is no evidence whatever for it and no imaginable reason for it to be true. The consensus of the survey articles (Bombieri 2000, Conrey 2003, and Sarnak 2008) is that the evidence for it is strong but not overwhelming, so that while it is probably true there is some reasonable doubt about it.
Some of the arguments for (or against) the Riemann hypothesis are listed by Sarnak (2008), Conrey (2003), and Ivić (2008), and include the following reasons.
- Several analogues of the Riemann hypothesis have already been proved. The proof of the Riemann hypothesis for varieties over finite fields by Deligne (1974) is possibly the single strongest theoretical reason in favor of the Riemann hypothesis. This provides some evidence for the more general conjecture that all zeta functions associated with automorphic forms satisfy a Riemann hypothesis, which includes the classical Riemann hypothesis as a special case. Similarly Selberg zeta functions satisfy the analogue of the Riemann hypothesis, and are in some ways similar to the Riemann zeta function, having a functional equation and an infinite product expansion analogous to the Euler product expansion. However there are also some major differences; for example they are not given by Dirichlet series. The Riemann hypothesis for the Goss zeta function was proved by Sheats (1998). In contrast to these positive examples, however, some Epstein zeta functions do not satisfy the Riemann hypothesis, even though they have an infinite number of zeros on the critical line (Titchmarsh 1986). These functions are quite similar to the Riemann zeta function, and have a Dirichlet series expansion and a functional equation, but the ones known to fail the Riemann hypothesis do not have an Euler product and are not directly related to automorphic representations.
- The numerical verification that many zeros lie on the line seems at first sight to be strong evidence for it. However analytic number theory has had many conjectures supported by large amounts of numerical evidence that turn out to be false. See Skewes number for a notorious example, where the first exception to a plausible conjecture related to the Riemann hypothesis probably occurs around 10316; a counterexample to the Riemann hypothesis with imaginary part this size would be far beyond anything that can currently be computed. The problem is that the behavior is often influenced by very slowly increasing functions such as log log T, that tend to infinity, but do so so slowly that this cannot be detected by computation. Such functions occur in the theory of the zeta function controlling the behavior of its zeros; for example the function S(T) above has average size around (log log T)1/2 . As S(T) jumps by at least 2 at any counterexample to the Riemann hypothesis, one might expect any counterexamples to the Riemann hypothesis to start appearing only when S(T) becomes large. It is never much more than 3 as far as it has been calculated, but is known to be unbounded, suggesting that calculations may not have yet reached the region of typical behavior of the zeta function.
- Denjoy's probabilistic argument for the Riemann hypothesis (Edwards 1974): If μ(x) is a random sequence of "1"s and "−1"s then, for every ε > 0, the function
-
- (the values of which are positions in a simple random walk) satisfies the bound
- with probability 1. The Riemann hypothesis is equivalent to this bound for the Möbius function μ and the Mertens function M derived in the same way from it. In other words, the Riemann hypothesis is in some sense equivalent to saying that μ(x) behaves like a random sequence of coin tosses. When μ(x) is non-zero its sign gives the parity of the number of prime factors of x, so informally the Riemann hypothesis says that the parity of the number of prime factors of an integer behaves randomly. Such probabilistic arguments in number theory often give the right answer, but tend to be very hard to make rigorous, and occasionally give the wrong answer for some results, such as Maier's theorem.
- The calculations in Odlyzko (1987) show that the zeros of the zeta function behave very much like the eigenvalues of a random Hermitian matrix, suggesting that they are the eigenvalues of some self-adjoint operator, which would imply the Riemann hypothesis. However all attempts to find such an operator have failed.
- There are several theorems, such as Goldbach's conjecture for sufficiently large odd numbers, that were first proved using the generalized Riemann hypothesis, and later shown to be true unconditionally. This could be considered as weak evidence for the generalized Riemann hypothesis, as several of its "predictions" turned out to be true.
- Lehmer's phenomenon (Lehmer 1956) where two zeros are sometimes very close is sometimes given as a reason to disbelieve in the Riemann hypothesis. However one would expect this to happen occasionally just by chance even if the Riemann hypothesis were true, and Odlyzko's calculations suggest that nearby pairs of zeros occur just as often as predicted by Montgomery's conjecture.
- Patterson (1988) suggests that the most compelling reason for the Riemann hypothesis for most mathematicians is the hope that primes are distributed as regularly as possible.
References
- Artin, Emil (1924), "Quadratische Körper im Gebiete der höheren Kongruenzen. II. Analytischer Teil", Mathematische Zeitschrift 19 (1): 207–246, doi:10.1007/BF01181075, ISSN 0025-5874
- Beurling, Arne (1955), "A closure problem related to the Riemann zeta-function", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 41: 312–314, doi:10.1073/pnas.41.5.312, MR0070655, ISSN 0027-8424, http://www.pnas.org/content/41/5/312.short
- Bohr, H.; Landau, E. (1914), "Ein Satz über Dirichletsche Reihen mit Anwendung auf die ζ-Funktion und die L-Funktionen", Rendiconti del Circolo Matematico di Palermo 37 (1): 269–272, doi:10.1007/BF03014823, ISSN 0009-725X
- Bombieri, Enrico (2000) (PDF), The Riemann Hypothesis - official problem description, Clay Mathematics Institute, http://www.claymath.org/millennium/Riemann_Hypothesis/riemann.pdf, retrieved 2008-10-25 Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Borwein, Peter; Choi, Stephen; Rooney, Brendan et al., eds. (2008), The Riemann Hypothesis: A Resource for the Afficionado and Virtuoso Alike, CMS Books in Mathematics, New York: Springer, doi:10.1007/978-0-387-72126-2, ISBN 978-0387721255
- Borwein, Peter; Ferguson, Ron; Mossinghoff, Michael J. (2008), "Sign changes in sums of the Liouville function", Mathematics of Computation 77 (263): 1681–1694, doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-08-02036-X, MR2398787, ISSN 0025-5718
- de Branges, Louis (1992), "The convergence of Euler products", Journal of Functional Analysis 107 (1): 122–210, doi:10.1016/0022-1236(92)90103-P, MR1165869, ISSN 0022-1236
- Cartier, P. (1982), "Comment l'hypothèse de Riemann ne fut pas prouvée", Seminar on Number Theory, Paris 1980-81 (Paris, 1980/1981), Progr. Math., 22, Boston, MA: Birkhäuser Boston, pp. 35–48, MR693308
- Connes, Alain (1999), "Trace formula in noncommutative geometry and the zeros of the Riemann zeta function", Selecta Mathematica. New Series 5 (1): 29–106, doi:10.1007/s000290050042, arXiv:math/9811068, MR1694895, ISSN 1022-1824
- Connes, Alain (2000), "Noncommutative geometry and the Riemann zeta function", Mathematics: frontiers and perspectives, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, pp. 35–54, MR1754766
- Conrey, J. B. (1989), "More than two fifths of the zeros of the Riemann zeta function are on the critical line", J. Reine angew. Math. 399: 1–16, MR1004130 , http://www.digizeitschriften.de/resolveppn/GDZPPN002206781
- Conrey, J. Brian (2003), "The Riemann Hypothesis" (PDF), Notices of the American Mathematical Society: 341–353, http://www.ams.org/notices/200303/fea-conrey-web.pdf Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Conrey, J. B.; Li, Xian-Jin (2000), "A note on some positivity conditions related to zeta and L-functions", International Mathematics Research Notices 2000 (18): 929–940, doi:10.1155/S1073792800000489, arXiv:math/9812166, MR1792282, ISSN 1073-7928
- Deligne, Pierre (1974), "La conjecture de Weil. I.", Publications Mathématiques de l'IHÉS 43: 273–307, doi:10.1007/BF02684373, MR0340258, ISSN 1618-1913, http://www.numdam.org/item?id=PMIHES_1974__43__273_0
- Deligne, Pierre (1980), "La conjecture de Weil : II.", Publications Mathématiques de l'IHÉS 52: 137–252, doi:10.1007/BF02684780, ISSN 1618-1913, http://www.numdam.org/item?id=PMIHES_1980__52__137_0
- Deninger, Christopher (1998), Some analogies between number theory and dynamical systems on foliated spaces, "Proceedings of the International Congress of Mathematicians, Vol. I (Berlin, 1998)", Documenta Mathematica: 163–186, MR1648030, ISSN 1431-0635, http://www.mathematik.uni-bielefeld.de/documenta/xvol-icm/00/Deninger.MAN.html
- Derbyshire, John (2003), Prime Obsession, Joseph Henry Press, Washington, DC, MR1968857, ISBN 978-0-309-08549-6
- Dyson, Freeman (2009), "Birds and frogs", Notices of the American Mathematical Society 56 (2): 212–223, MR2483565, ISSN 0002-9920, http://www.ams.org/notices/200902/rtx090200212p.pdf
- Edwards, H. M. (1974), Riemann's Zeta Function, New York: Dover Publications, MR0466039, ISBN 978-0-486-41740-0
- Ford, Kevin (2002), "Vinogradov's integral and bounds for the Riemann zeta function", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. Third Series 85 (3): 565–633, doi:10.1112/S0024611502013655, MR1936814, ISSN 0024-6115
- Franel, J.; Landau, E. (1924), "Les suites de Farey et le problème des nombres premiers", Göttinger Nachr.: 198–206
- Gourdon, Xavier (2004) (PDF), The 1013 first zeros of the Riemann Zeta function, and zeros computation at very large height, http://numbers.computation.free.fr/Constants/Miscellaneous/zetazeros1e13-1e24.pdf
- Gram, J. P. (1903), "Note sur les zéros de la fonction ζ(s) de Riemann", Acta Mathematica 27: 289–304, doi:10.1007/BF02421310
- Hadamard, Jacques (1896), "Sur la distribution des zéros de la fonction ζ(s) et ses conséquences arithmétiques", Bulletin Société Mathématique de France 14: 199–220, http://www.numdam.org/item?id=BSMF_1896__24__199_1 Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Hardy, G. H. (1914), "Sur les Zéros de la Fonction ζ(s) de Riemann", C. R. Acad. Sci. Paris 158: 1012–1014, JFM 45.0716.04, http://gallica.bnf.fr/ark:/12148/bpt6k3111d.image.f1014.langEN Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Hardy, G. H.; Littlewood, J. E. (1921), "The zeros of Riemann's zeta-function on the critical line", Math. Z. 10: 283–317, doi:10.1007/BF01211614
- Haselgrove, C. B. (1958), "A disproof of a conjecture of Pólya", Mathematika 5: 141–145, doi:10.1112/S0025579300001480, MR0104638 Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Haselgrove, C. B.; Miller, J. C. P. (1960), Tables of the Riemann zeta function, Royal Society Mathematical Tables, Vol. 6, Cambridge University Press, MR0117905, ISBN 978-0-521-06152-0Review
- Hutchinson, J. I. (1925), "On the Roots of the Riemann Zeta-Function", Transactions of the American Mathematical Society 27 (1): 49–60, doi:10.2307/1989163, ISSN 0002-9947, http://www.jstor.org/stable/1989163
- Ingham, A.E. (1932), The Distribution of Prime Numbers, Cambridge Tracts in Mathematics and Mathematical Physics, 30, Cambridge University Press. Reprinted 1990, ISBN 978-0-521-39789-6, MR1074573
- Ivić, A. (1985), The Riemann Zeta Function, New York: John Wiley & Sons, MR0792089, ISBN 978-0-471-80634-9 (Reprinted by Dover 2003)
- Ivić, Aleksandar (2008), "On some reasons for doubting the Riemann hypothesis", in Borwein, Peter; Choi, Stephen; Rooney, Brendan et al., The Riemann Hypothesis: A Resource for the Afficionado and Virtuoso Alike, CMS Books in Mathematics, New York: Springer, pp. 131–160, arXiv:math.NT/0311162, ISBN 978-0387721255
- Karatsuba, A. A.; Voronin, S. M. (1992), The Riemann zeta-function, de Gruyter Expositions in Mathematics, 5, Berlin: Walter de Gruyter & Co., MR1183467, ISBN 978-3-11-013170-3
- Keating, Jonathan P.; Snaith, N. C. (2000), "Random matrix theory and ζ(1/2+it)", Communications in Mathematical Physics 214 (1): 57–89, doi:10.1007/s002200000261, MR1794265, ISSN 0010-3616
- Knauf, Andreas (1999), "Number theory, dynamical systems and statistical mechanics", Reviews in Mathematical Physics. A Journal for Both Review and Original Research Papers in the Field of Mathematical Physics 11 (8): 1027–1060, doi:10.1142/S0129055X99000325, MR1714352, ISSN 0129-055X
- von Koch, Helge (1901), "Sur la distribution des nombres premiers", Acta Mathematica 24: 159–182, doi:10.1007/BF02403071
- Kurokawa, Nobushige (1992), "Multiple zeta functions: an example", Zeta functions in geometry (Tokyo, 1990), Adv. Stud. Pure Math., 21, Tokyo: Kinokuniya, pp. 219–226, MR1210791
- Lapidus, Michel L. (2008), In search of the Riemann zeros, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, MR2375028, ISBN 978-0-8218-4222-5, http://www.ams.org/bookstore-getitem/item=mbk-51
- Lavrik, A. F. (2001), "Zeta-function", in Hazewinkel, Michiel, Encyclopaedia of Mathematics, Springer, ISBN 978-1556080104, http://eom.springer.de/Z/z099260.htm
- Lehmer, D. H. (1956), "Extended computation of the Riemann zeta-function", Mathematika. A Journal of Pure and Applied Mathematics 3: 102–108, doi:10.1112/S0025579300001753, MR0086083, ISSN 0025-5793
- Levinson, N. (1974), "More than one-third of the zeros of Riemann's zeta function are on σ = 1/2", Adv. In Math. 13: 383–436, doi:10.1016/0001-8708(74)90074-7, MR0564081
- Littlewood, J. E. (1962), "The Riemann hypothesis", The scientist speculates: an anthology of partly baked idea, New York: Basic books
- van de Lune, J.; te Riele, H. J. J.; Winter, D. T. (1986), "On the zeros of the Riemann zeta function in the critical strip. IV", Mathematics of Computation 46 (174): 667–681, doi:10.2307/2008005, MR829637, ISSN 0025-5718, http://www.jstor.org/stable/2008005
- Massias, J.-P.; Nicolas, Jean-Louis; Robin, G. (1988), "Évaluation asymptotique de l'ordre maximum d'un élément du groupe symétrique", Polska Akademia Nauk. Instytut Matematyczny. Acta Arithmetica 50 (3): 221–242, MR960551, ISSN 0065-1036, http://matwbn.icm.edu.pl/tresc.php?wyd=6&tom=50&jez=
- Montgomery, Hugh L. (1973), "The pair correlation of zeros of the zeta function", Analytic number theory, Proc. Sympos. Pure Math., XXIV, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, pp. 181–193, MR0337821 Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Montgomery, Hugh L. (1983), "Zeros of approximations to the zeta function", in Erdős, Paul, Studies in pure mathematics. To the memory of Paul Turán., Basel, Boston, Berlin: Birkhäuser, pp. 497–506, MR820245, ISBN 978-3-7643-1288-6
- Nicely, Thomas R. (1999), "New maximal prime gaps and first occurrences", Mathematics of Computation 68 (227): 1311–1315, doi:10.1090/S0025-5718-99-01065-0, MR1627813, http://www.trnicely.net/gaps/gaps.html.
- Nyman, Bertil (1950), On the One-Dimensional Translation Group and Semi-Group in Certain Function Spaces, PhD Thesis, University of Uppsala: University of Uppsala, MR0036444
- Odlyzko, A. M.; te Riele, H. J. J. (1985), "Disproof of the Mertens conjecture", Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 357: 138–160, MR783538, ISSN 0075-4102, http://gdz.sub.uni-goettingen.de/no_cache/dms/load/img/?IDDOC=262633
- Odlyzko, A. M. (1987), "On the distribution of spacings between zeros of the zeta function", Mathematics of Computation 48 (177): 273–308, doi:10.2307/2007890, MR866115, ISSN 0025-5718, http://www.jstor.org/stable/2007890
- Odlyzko, A. M. (1990), "Bounds for discriminants and related estimates for class numbers, regulators and zeros of zeta functions: a survey of recent results", Séminaire de Théorie des Nombres de Bordeaux. Série 2 2 (1): 119–141, MR1061762, ISSN 0989-5558, http://www.numdam.org/item?id=JTNB_1990__2_1_119_0
- Odlyzko, A. M. (1992), The 1020-th zero of the Riemann zeta function and 175 million of its neighbors, http://www.dtc.umn.edu/~odlyzko/unpublished/index.html This unpublished book describes the implementation of the algorithm and discusses the results in detail.
- Patterson, S. J. (1988), An introduction to the theory of the Riemann zeta-function, Cambridge Studies in Advanced Mathematics, 14, Cambridge University Press, MR933558, ISBN 978-0-521-33535-5
- Riemann, Bernhard (1859), "Ueber die Anzahl der Primzahlen unter einer gegebenen Grösse", Monatsberichte der Berliner Akademie, http://www.maths.tcd.ie/pub/HistMath/People/Riemann/Zeta/. In Gesammelte Werke, Teubner, Leipzig (1892), Reprinted by Dover, New York (1953). Original manuscript (with English translation). Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008) and (Edwards 1874)
- Riesel, Hans; Göhl, Gunnar (1970), "Some calculations related to Riemann's prime number formula", Mathematics of Computation 24 (112): 969–983, doi:10.2307/2004630, MR0277489, ISSN 0025-5718, http://jstor.org/stable/2004630
- Riesz, M. (1916), "Sur l'hypothèse de Riemann", Acta Mathematica 40: 185–190, doi:10.1007/BF02418544
- Robin, G. (1984), "Grandes valeurs de la fonction somme des diviseurs et hypothèse de Riemann", Journal de Mathématiques Pures et Appliquées. Neuvième Série 63 (2): 187–213, MR774171, ISSN 0021-7824
- Rockmore, Dan (2005), Stalking the Riemann hypothesis, Pantheon Books, MR2269393, ISBN 978-0-375-42136-5
- Rosser, J. Barkley; Yohe, J. M.; Schoenfeld, Lowell (1969), "Rigorous computation and the zeros of the Riemann zeta-function. (With discussion)", Information Processing 68 (Proc. IFIP Congress, Edinburgh, 1968), Vol. 1: Mathematics, Software, Amsterdam: North-Holland, pp. 70–76, MR0258245
- Sabbagh, Karl (2003), The Riemann hypothesis, Farrar, Straus and Giroux, New York, MR1979664, ISBN 978-0-374-25007-2
- Salem, Raphaël (1953), "Sur une proposition équivalente à l'hypothèse de Riemann", Les Comptes rendus de l'Académie des sciences 236: 1127–1128, MR0053148
- Sarnak, Peter (2008), "Problems of the Millennium: The Riemann Hypothesis", in Borwein, Peter; Choi, Stephen; Rooney, Brendan et al. (PDF), The Riemann Hypothesis: A Resource for the Afficionado and Virtuoso Alike, CMS Books in Mathematics, New York: Springer, pp. 107–115, ISBN 978-0387721255, http://www.claymath.org/millennium/Riemann_Hypothesis/Sarnak_RH.pdf
- du Sautoy, Marcus (2003), The music of the primes, HarperCollins Publishers, MR2060134, ISBN 978-0-06-621070-4
- Schoenfeld, Lowell (1976), "Sharper bounds for the Chebyshev functions θ(x) and ψ(x). II", Mathematics of Computation 30 (134): 337–360, doi:10.2307/2005976, MR0457374, ISSN 0025-5718, http://jstor.org/stable/2005976
- Selberg, Atle (1942), "On the zeros of Riemann's zeta-function.", Skr. Norske Vid. Akad. Oslo I. 10: 59 pp, MR0010712
- Selberg, Atle (1946), "Contributions to the theory of the Riemann zeta-function", Arch. Math. Naturvid. 48 (5): 89–155, MR0020594
- Selberg, Atle (1956), "Harmonic analysis and discontinuous groups in weakly symmetric Riemannian spaces with applications to Dirichlet series", J. Indian Math. Soc. (N.S.) 20: 47–87, MR0088511
- Sheats, Jeffrey T. (1998), "The Riemann hypothesis for the Goss zeta function for Fq[T]", Journal of Number Theory 71 (1): 121–157, doi:10.1006/jnth.1998.2232, MR1630979, ISSN 0022-314X
- Siegel, C. L. (1932), "Über Riemanns Nachlaß zur analytischen Zahlentheorie", Quellen Studien zur Geschichte der Math. Astron. und Phys. Abt. B: Studien 2: 45–80 Reprinted in Gesammelte Abhandlungen, Vol. 1. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1966.
- Stein, William; Mazur, Barry (2007) (PDF), What is Riemann’s Hypothesis?, http://modular.math.washington.edu/edu/2007/simuw07/notes/rh.pdf
- Titchmarsh, Edward Charles (1935), "The Zeros of the Riemann Zeta-Function", Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences (The Royal Society) 151 (873): 234–255, doi:10.1098/rspa.1935.0146, ISSN 0080-4630, http://www.jstor.org/stable/96545
- Titchmarsh, Edward Charles (1936), "The Zeros of the Riemann Zeta-Function", Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences (The Royal Society) 157 (891): 261–263, doi:10.1098/rspa.1936.0192, ISSN 0080-4630, http://www.jstor.org/stable/96692
- Titchmarsh, Edward Charles (1986), The theory of the Riemann zeta-function (2nd ed.), The Clarendon Press Oxford University Press, MR882550, ISBN 978-0-19-853369-6
- Turán, Paul (1948), "On some approximative Dirichlet-polynomials in the theory of the zeta-function of Riemann", Danske Vid. Selsk. Mat.-Fys. Medd. 24 (17): 36, MR0027305 Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Turing, Alan M. (1953), "Some calculations of the Riemann zeta-function", Proceedings of the London Mathematical Society. Third Series 3: 99–117, doi:10.1112/plms/s3-3.1.99, MR0055785, ISSN 0024-6115
- de la Vallée-Poussin, Ch.J. (1896), "Recherches analytiques sur la théorie des nombers premiers", Ann. Soc. Sci. Bruxelles 20: 183–256
- de la Vallée-Poussin, Ch.J. (1899–1900), "Sur la fonction ζ(s) de Riemann et la nombre des nombres premiers inférieurs à une limite donnée", Mem. Couronnes Acad. Sci. Belg. 59 (1) Reprinted in (Borwein et al. 2008).
- Weil, André (1948), Sur les courbes algébriques et les variétés qui s'en déduisent, Actualités Sci. Ind., no. 1041 = Publ. Inst. Math. Univ. Strasbourg 7 (1945), Hermann et Cie., Paris, MR0027151
- Weil, André (1949), "Numbers of solutions of equations in finite fields", Bulletin of the American Mathematical Society 55: 497–508, doi:10.1090/S0002-9904-1949-09219-4, MR0029393, ISSN 0002-9904, http://www.ams.org/bull/1949-55-05/S0002-9904-1949-09219-4/home.html Reprinted in Oeuvres Scientifiques/Collected Papers by Andre Weil ISBN 0-387-90330-5
- Weinberger, Peter J. (1973), "On Euclidean rings of algebraic integers", Analytic number theory ( St. Louis Univ., 1972), Proc. Sympos. Pure Math., 24, Providence, R.I.: Amer. Math. Soc., pp. 321–332, MR0337902
- Wiles, Andrew (2000), "Twenty years of number theory", Mathematics: frontiers and perspectives, Providence, R.I.: American Mathematical Society, pp. 329–342, MR1754786, ISBN 978-0-8218-2697-3
- Zagier, Don (1977), "The first 50 million prime numbers" (PDF), Math. Intelligencer (Springer) 0: 7--19, doi:10.1007/BF03039306, MR643810, http://modular.math.washington.edu/edu/2007/simuw07/misc/zagier-the_first_50_million_prime_numbers.pdf
- Zagier, Don (1981), "Eisenstein series and the Riemann zeta function", Automorphic forms, representation theory and arithmetic (Bombay, 1979), Tata Inst. Fund. Res. Studies in Math., 10, Tata Inst. Fundamental Res., Bombay, pp. 275–301, MR633666
External links
- American institute of mathematics, Riemann hypothesis
- Apostol, Tom, Where are the zeros of zeta of s?, http://www.math.wisc.edu/~robbin/funnysongs.html#Zeta Poem about the Riemann hypothesis, sung by John Derbyshire.
- Borwein, Peter (PDF), The Riemann Hypothesis, http://oldweb.cecm.sfu.ca/~pborwein/COURSE/MATH08/LECTURE.pdf (Slides for a lecture)
- Conrad, K. (2010), Consequences of the Riemann hypothesis, http://mathoverflow.net/questions/17232
- Conrey, J. Brian; Farmer, David W, Equivalences to the Riemann hypothesis, http://aimath.org/pl/rhequivalences
- Gourdon, Xavier; Sebah, Pascal (2004), Computation of zeros of the Zeta function, http://numbers.computation.free.fr/Constants/Miscellaneous/zetazeroscompute.html (Reviews the GUE hypothesis, provides an extensive bibliography as well).
- Odlyzko, Andrew, Home page, http://www.dtc.umn.edu/~odlyzko/ including papers on the zeros of the zeta function and tables of the zeros of the zeta function
- Odlyzko, Andrew (2002) (PDF), Zeros of the Riemann zeta function: Conjectures and computations, http://www.dtc.umn.edu/~odlyzko/talks/riemann-conjectures.pdf Slides of a talk
- Pegg, Ed (2004), Ten Trillion Zeta Zeros, Math Games website, http://www.maa.org/editorial/mathgames/mathgames_10_18_04.html A discussion of Xavier Gourdon's calculation of the first ten trillion non-trivial zeros
- Pugh, Glen, Java applet for plotting Z(t), http://web.viu.ca/pughg/RiemannZeta/RiemannZetaLong.html
- Rubinstein, Michael, algorithm for generating the zeros, http://pmmac03.math.uwaterloo.ca/~mrubinst/l_function_public/L.html.
- du Sautoy, Marcus (2006), Prime Numbers Get Hitched, Seed Magazine, http://www.seedmagazine.com/news/2006/03/prime_numbers_get_hitched.php
- Stein, William A., What is Riemann's hypothesis, http://modular.math.washington.edu/edu/2007/simuw07/index.html
- de Vries, Andreas (2004), The Graph of the Riemann Zeta function ζ(s), http://math-it.org/Mathematik/Riemann/RiemannApplet.html, a simple animated Java applet.
- Watkins, Matthew R. (2007-07-18), Proposed proofs of the Riemann Hypothesis, http://secamlocal.ex.ac.uk/~mwatkins/zeta/RHproofs.htm
- Zetagrid (2002) A distributed computing project that attempted to disprove Riemann's hypothesis; closed in November 2005